An enlarged prostate is a known problem in men. As they age, the chances of this problem increase considerably. A man in his 60s has a 50% chance of having an enlarged prostate. Seeking enlarged prostate treatment is determined by the severity of the issue after identifying it. The problem may go unnoticed if the symptoms are mild and manageable.
Let’s see what the prostate enlargement symptoms and treatments are.
What is the prostate?
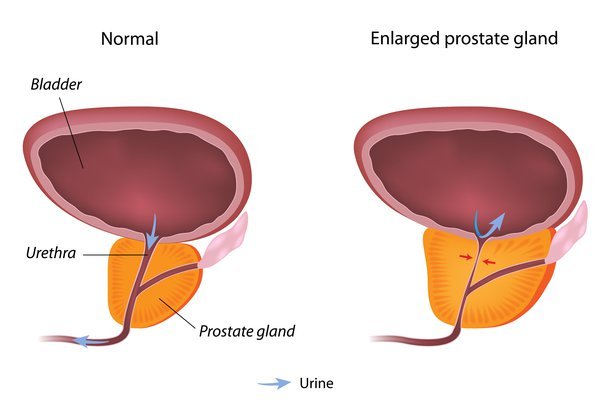
Prostate is a gland that is located at the bottom of the bladder in men. It is small in size, approximately the size of a walnut. Its size stays the same until the age of 40 and starts to increase. The size can increase up to that of a lemon or an apricot. Through the middle of the prostate runs the urethra, which is a tube that empties the bladder.
The prostate produces prostatic fluid. This fluid has proteins, enzymes, and minerals essential for sperm functioning properly. In addition to this role, the prostate closes the urethra during ejaculation to prevent semen from entering the bladder.
Symptoms of an enlarged prostate
When the prostate grows beyond its regular size, it is termed enlarged. It is called the Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and is not cancerous. The issues caused by this condition will require you to seek enlarged prostate treatment. However, an enlarged prostate in itself may not be the issue. Its position in relation to the urethra will also determine if it is a problem or not. The symptoms of an enlarged prostate are:
- A sudden need to urinate
- An interrupted or weak urinary flow
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty in initiating urine flow even with a full bladder
- Being unable to completely empty the bladder while urinating
- Pain after urinating
- Inability to control the bladder
The above-listed symptoms might be similar to those of overactive bladder (OAB) or bladder cancer. It is advised to consult a doctor to identify the condition. An enlarged prostate may also present itself without any noticeable symptoms.
Treatment procedures for enlarged prostate
Various procedures ranging from non-invasive to invasive can be used for enlarged prostate treatment. If the problems are minor or barely there, you can manage the condition by consulting a doctor and going for a procedure if the condition worsens.
These are the treatment procedures for an enlarged prostate:
- Medication
In the case of mild symptoms, certain medications can help with the condition. Your doctor may prescribe medicines to stop the prostate’s growth or shrink it to reduce the symptoms. The medication may include:
- Alpha-blockers- They relax the prostate and bladder neck’s smooth muscles to help improve urine flow and reduce blockage.
- Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors- They lessen the urinary tract’s symptoms by relaxing the smooth muscles.
- Dutasteride- It can block the production of DHT (Dihydrotestosterone), which can cause prostate enlargement. It, therefore, slows down and, in some cases, reverses the prostate’s growth.
- Minimally invasive procedures
These are as follows:
- Transurethral Microwave Therapy (TUMT)- In this, a tiny microwave antenna is inserted into the urethra through the penis. It is inserted to the point where the urethra is surrounded by the prostate. The microwave energy emitted by the antenna destroys the excess prostate tissue.
- Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA)- In the minimally invasive enlarged prostate treatment TUNA, radiofrequency needles are placed in the part of the prostate pressing against the urethra. The needles are placed through the urethra. Radio waves sent through the needles shrink the prostate by destroying the excess tissue.
- Prostate laser surgery- Different types of laser surgeries can be a treatment here. Photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP) uses a laser to vaporize the excess tissue of the prostate. It is used in cases that range from mild to moderate. Holmium laser ablation of the prostate (HoLAP) uses a different kind of laser, but the method is the same.
- Surgery for moderate to severe cases
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)- In this procedure, a resectoscope is inserted into the urethra through the penis. The resectoscope is used to cut the excess prostate tissue from the inside. This procedure is done if the medication hasn’t helped. Recovery time for this is more than the other procedures.
- Open prostatectomy- In this procedure, the surgeon cuts the lower abdomen to reach the bladder and the prostate. He then removes the enlarged portion of the prostate.
- Laser surgery- Some laser surgeries require cutting the excess tissue instead of reducing its size. One such surgery is Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP). A laser cuts the excess tissue, which is then cut into smaller pieces with another instrument and removed. This surgery is done when the case is severe.
- Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP)- This is not surgery to remove the excess prostate tissue. General anesthesia (completely unconscious) or regional anesthesia (numb from the waist and below) are given to the patient. Incisions are made in the prostate to relieve pressure on the urethra and allow urination more easily.
These are some of the possible options for enlarged prostate treatment. Your doctor can also recommend other procedures depending on the symptoms and severity. Consult a doctor for diagnosis and the best possible treatment for you.
Read More Blogs: